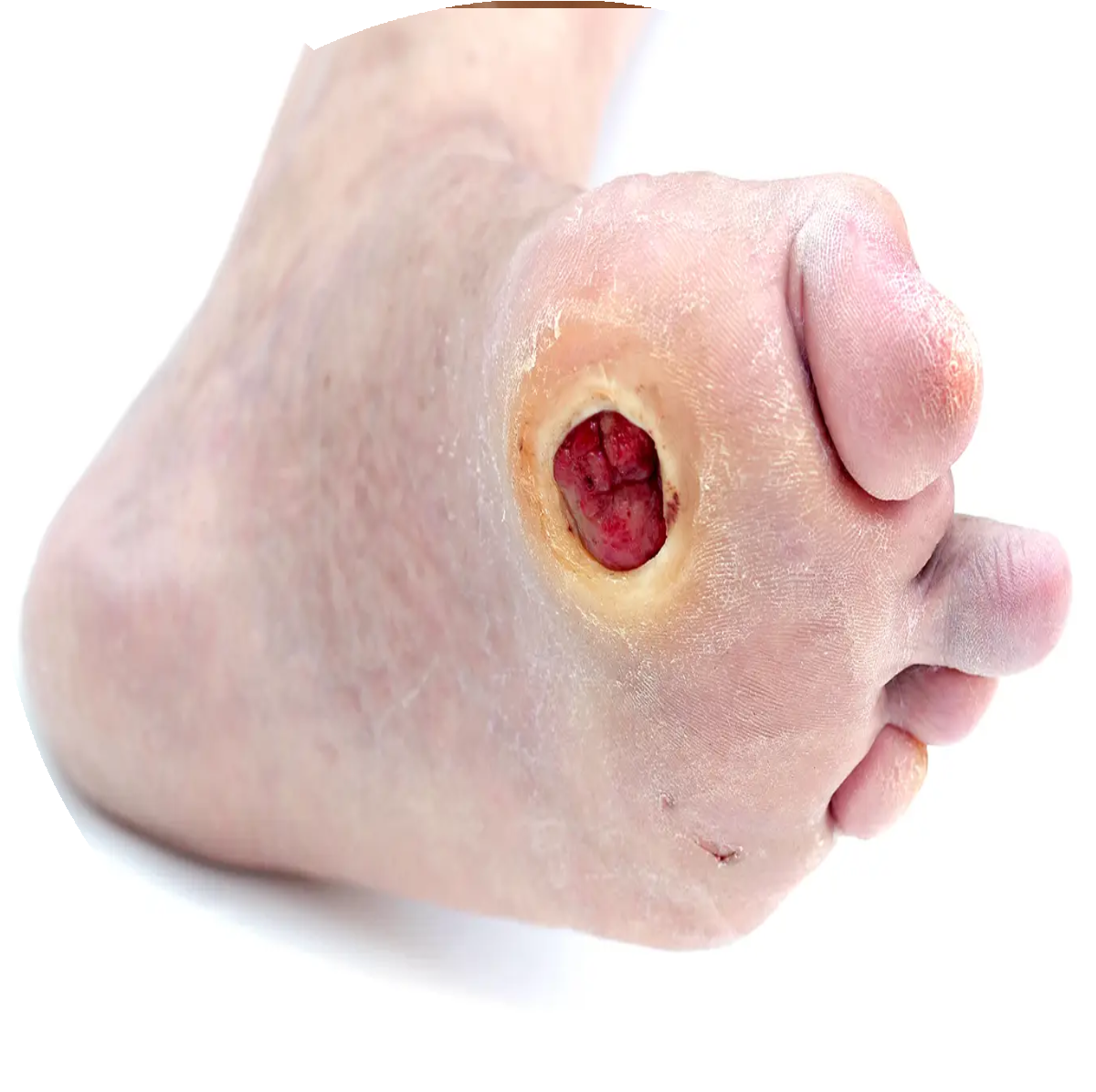
Foot disease affects about 6% of people with diabetes and includes ulcer, infection, or rupture of the fingers. It can affect social participation and livelihood and impair the quality of life of a patient.
The diabetic foot is a severe complication of diabetes that affects one foot of the ulcer that is associated with neuropathy or peripheral artery disease of the lower limb in diabetic patients. Most of the ulcers will heal, while some of them will remain active and some of them will finally lead to potential limb amputation within 6-18 months after the evaluation.
With age and duration of diabetes, the risk of leg ulcers and limb dissection increases. The management of diabetic foot involves a multidisciplinary approach.
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can cause foot problems. It damages the peripheral nerves and blood vessels, and causes problems in your feet and legs. Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to two main conditions, including peripheral artery disease and peripheral neuropathy, through complex metabolic pathways.

The main cause of diabetic foot is the high blood sugar levels in the body, which damages the nerves. This nerve damage results in a loss of sensation in the feet.
This, in turn, has a cascading effect where the person is unable to feel any wound or irritation in the feet, which can result in untreated infections. These, if allowed to fester, can lead to more serious complications such as gangrene, and can require amputation.
Symptoms of Diabetic Foot:
- Discolouration of the skin
- Swelling or redness
- Discharge of pus or other fluids
- Foul odour from the wound
- Changes in the toenails
Book an appointment
If you feel that we can be of any assistance please take a moment to fill out the enquiry form below and one of our staff members will answer your question as soon as possible.
Visit us anytime
We care for your well being. We are always available for you.
Address
Delhi 110076